This page discusses the parties involved in a letter of credit. Each L/C party will be presented briefly, and its roles and responsibilities will be explained with the help of the graphic illustrations. A video on this topic is also available.
A Letter of Credit (LC) is a financial instrument in international trade that guarantees payment to the seller (beneficiary) as long as the agreed-upon terms and conditions are met.
It involves multiple parties, each playing a distinct role.
The key parties in an LC transaction include the beneficiary (seller), applicant (buyer), issuing bank, advising bank, confirming bank, nominated bank, and reimbursing bank. Understanding the roles and responsibilities of these entities ensures smooth and hassle-free letter of credit operations for businesses.
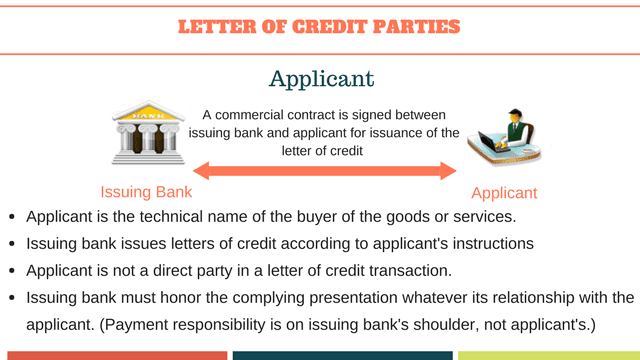
Applicant
Applicant is the buyer of the goods or services supplied by the seller.
Letter of credit is opened by the issuing bank as per applicant’s request. However, applicant does not belong one of the parties to a letter of credit transaction.
This is because of the fact that letters of credit are separate transactions from the sale or other contract on which they may be based.
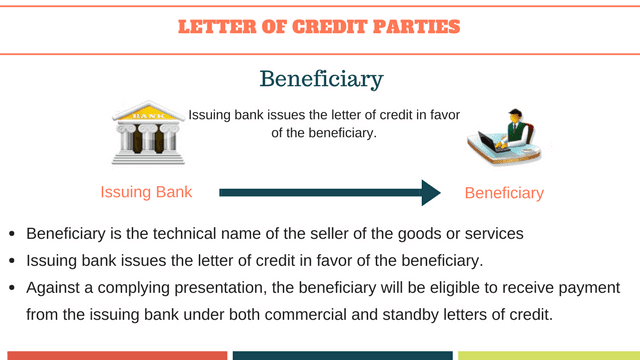
Beneficiary
Beneficiary is the seller of the goods or the provider of the services in a standard commercial letter of credit transaction.
Letter of credit is opened by the issuing bank in favor of the beneficiary.
Beneficiaries will be eligible to receive payment under both commercial and standby letters of credit, as long as they make complying presentations.
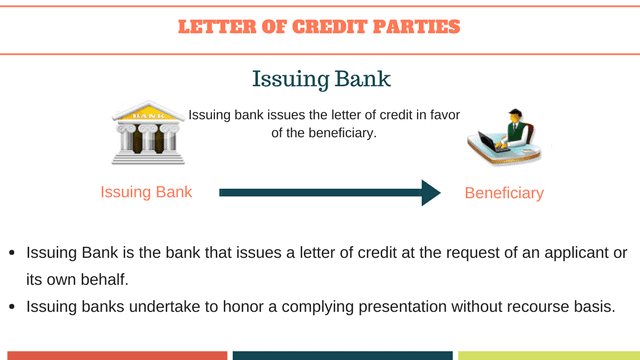
Issuing Bank
Issuing Bank is the bank that issues a letter of credit at the request of an applicant or its own behalf.
Issuing bank undertakes to honor a complying presentation of the beneficiary without recourse.
Which means that issuing banks must pay the letter of credit amount to the beneficiaries, if complying presentation has been made.
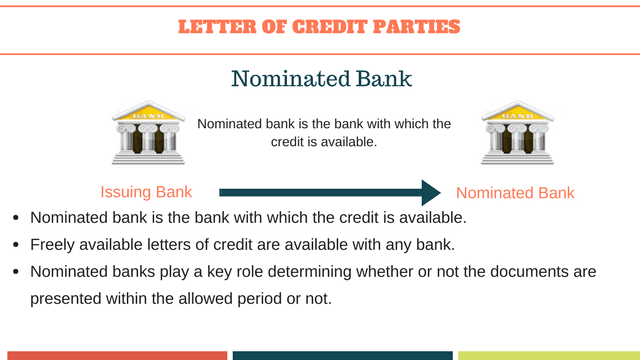
Nominated Bank
Nominated bank is the bank with which the credit is available or any bank in the case of a credit available with any bank.
Nominated banks play a key role determining whether or not the documents are presented within the allowed period or not.
Advising Bank
Advising bank is the bank that advises the credit at the request of the issuing bank.
An advising bank that is not a confirming bank advises the credit and any amendment without any obligation to honor.
By advising the credit or amendment, the advising bank signifies that it has satisfied itself as to the apparent authenticity of the credit or amendment and that the advice accurately reflects the terms and conditions of the credit.
Confirming Bank
Confirming bank is the bank that adds its confirmation to a credit upon the issuing bank’s authorization or request.
Confirming bank may or may not add its confirmation to a letter of credit. This decision is up to confirming bank only.
However, once it adds its confirmation to the credit confirming is irrevocably bound to honor or negotiate as of the time it adds its confirmation to the credit.
Even if the issuing bank fails to honor, confirming bank must pay to the beneficiary.
Reimbursing Bank
Reimbursing Bank shall mean the bank instructed and/or authorized to provide reimbursement pursuant to a reimbursement authorization issued by the issuing bank.
Reimbursing Bank is the settlement bank between the issuing bank and the nominated bank or the confirming bank.
If letter of credit currency is USD, reimbursing bank is usually located in US. If letter of credit currency is EUR, reimbursing bank is generally located in Germany.
ÖZGÜR EKER (CDCS)
Letter of Credit Consultancy Services
