Letters of credit (l/c) and cash against documents (documentary collections, cad) are both payment methods in international trade.
Their combined share is around 50% in all trade finance practices.
Letters of credit and cash against documents have some similarities. We can identify major common points of these two payment methods as follows:
- Both payment methods are executed by banks,
- Documents play a key role under both payment options,
- Both of them are governed by internationally accepted rules.
Despite these similarities they have significant differences as well.
On this article I would like to identify the main differences between Letters of credit (l/c) and cash against documents (documentary collections, cad).
What are the Main Differences Between Cash Against Documents and Letters of Credit?
Let us examine the differences between these two important payment methods of international trade article by article below.
Governing Rules: Letters of credit transactions are governed by UCP 600 and cash against documents are governed by URC 522 rules. You can get detailed information regarding these two sets of rules by reading my related articles.
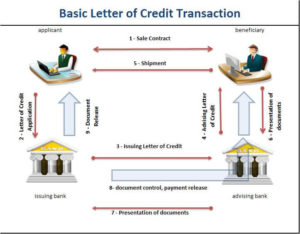
Transaction Flow: Letters of credit are opened by the issuing banks with the request and authorization which they have received from the applicants.
Applicant is the importer in a commercial letter of credit. As a result letters of credit are initiated by the importers.
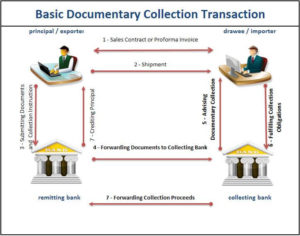
On the other hand, cash against documents or documentary collections as we called them in trade finance are initiated by the exporters.
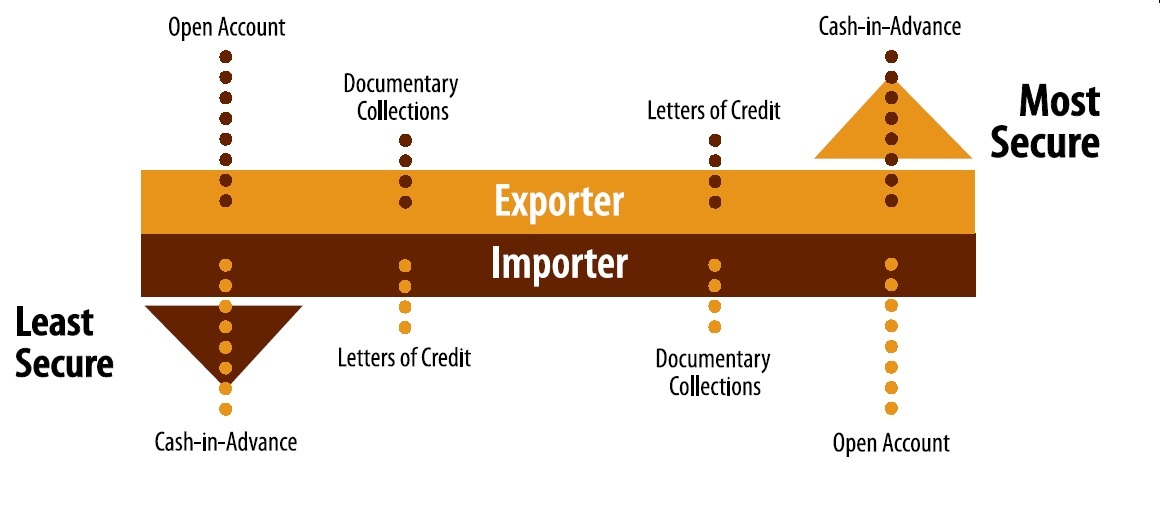
Risk Degree: Letters of credit give more assurance to the exporters than cash against documents. For this reason the letter of credit is accepted as a more secure payment method in international trade than the documentary collection.
Responsibilities of Banks : Banks play a key role in letters of credit transactions and they have high levels of responsibilities against the exporters.
On the other hand in documentary collections banks have almost no valid responsibilities against the exporters.
As an example, the banks do not control the documents in documentary collections, but in documentary credit transactions banks check the documents to determine whether the presentation is complying or not.
Complexity : Documentary collections are much more easy in operational perspective than letters of credit.
Cost : The costs of the documentary collections are less than the cost of the documentary credits.
Letters of credit are one of the most expensive payment methods in international trade.
Please read my article for detailed information : How to deal with high banking commissions under letters of credit as an exporter?