Canada, second largest country in the world in area (after Russia), occupying roughly the northern two-fifths of the continent of North America.(1)
Canada borders with the United States as well as a long maritime boundary with Denmark, at the autonomous island country of Greenland, and a short maritime border with France, at the overseas islands of Saint Pierre and Miquelon.(2)
Canada is one of the leading exporters of agricultural and non-agricultural commodities such as crude and refined petroleum, gold, lumber, aluminum, paper, wheat, colza seeds and oil, dried legumes etc.
Canada is a member of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC), the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), and the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP).(3)
On this page you can find brief information in regards to Canada economy, key points of its international trade, banks in Canada and letter of credit usage tips specific to Canada.
Canada Exports at a Glance:
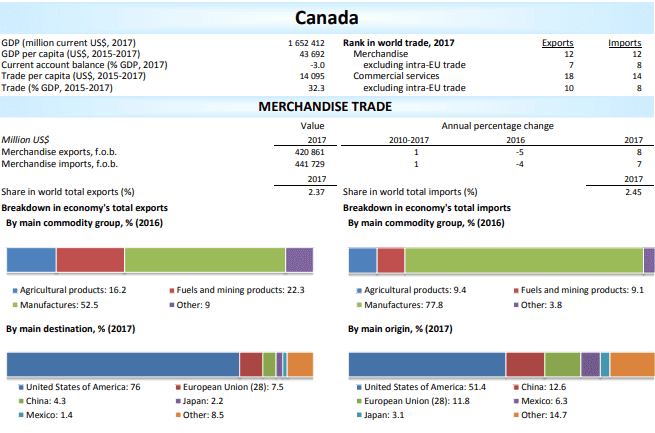
As of 2017 Canada is the 12th biggest exporting country in the world. Canada’s 2017 exports declared as 420 billion US dollars in value.
Breakdown of Canada’s total exports by main commodity groups are: agricultural products %16.2, fuels and mining products %22.3, manufactures %52.5.
The most significant export destinations of Canada are United States of America %76, European Union %7.5, China %4.3, Japan %2.2 and Mexico %1.4.
Top Exported Products of Canada (2017)