Letter of credit is one of the payment methods in international trade. Just like other payment methods it has certain advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of letter of credit:
- It simply works: In some situations, letter of credit works when other payment options not.
- It is a balanced payment option: Importers and exporters could reach reasonable payment terms via letter of credit.
Disadvantages of a letter of credit:
- It is expensive: Both exporters and importers have to pay high fees when choosing the letter of credit as a payment option.
- It is difficult: Letters of credit requires experienced stuff who possess certain amount of trade finance knowledge.
After explaining the advantages and disadvantages of a letter of credit briefly, we can now proceed for further descriptions.
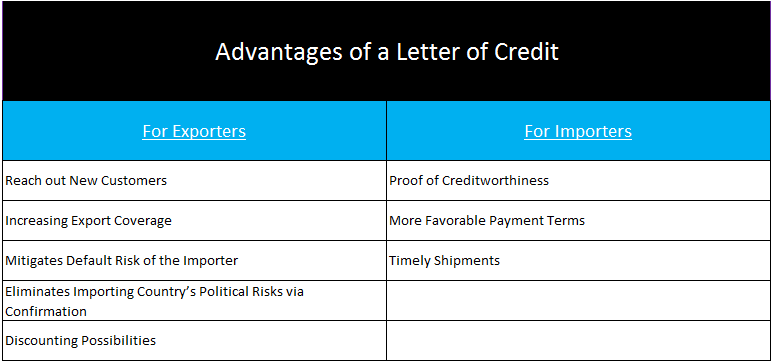
Advantages of a Letter of Credit:
For Exporters:
- Reach out New Customers: Establishing a new business connection is not easy. It is difficult to find a new buyer who is ready to make an advance payment to an untested exporter. By offering a letter of credit, the exporter can increase the chance of securing the order.
- Increasing Export Coverage: Exporters can increase their export coverage by regional means if they can effectively use letters of credit. For example, letter of credit is the main payment option for majority of the Middle East countries.
- Mitigates Default Risk of the Importer: By using a letter of credit, the exporter can replace default risk from the importer to the importer’s bank, because the letter of credit is a conditional payment undertaking of the issuing bank.
- Eliminates Importing Country’s Political Risks via Confirmation: By adding confirmation, the exporter can eliminate importing country’s political risks, at least in theory. For further information please read our post “Confirmation and Confirmed Letter of Credit“.
- Discounting Possibilities: It is possible to discount letters of credit that do not payable at sight. Once the issuing bank or confirming banks determines that the letter of credit documents are complying, the respected bank can discount the credit.
For Importers:
- Proof of Creditworthiness: By issuing a letter of credit from a reputable bank, the importer proves that he is a financially reputable company.
- More Favorable Payment Terms: The importer may be able to convince the exporter to work with a deferred payment terms instead of an at sight payment via a letter of credit. As the exporter can discount the credit any time after the complying presentation, deferred payment should not a big issue for him. Most frequently used deferred payment options under the letters of credit are 30 days, 60 days or 90 days after the bill of lading date.
- Timely Shipments: Importers can determine the shipment period by using a letter of credit. If the exporter can not shipped the goods on time, he may face a late shipment discrepancy.
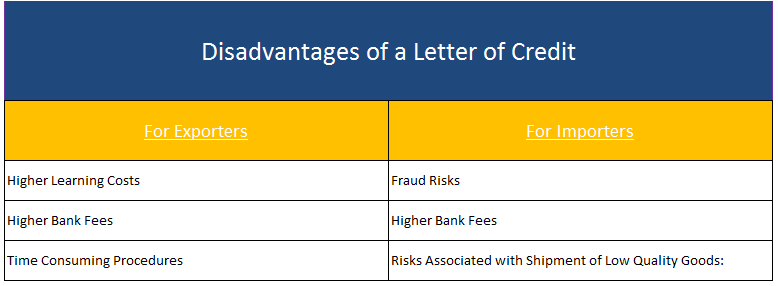
Disadvantages of a Letter of Credit:
For Exporters:
- Higher Learning Costs: Letter of credit is one of the most complex fields of the international trade. Exporters acting with lack of letter of credit expertise and experience may face unpleasant consequences.
- Higher Bank Fees: Exporters may have to pay high letter of credit fees to the banks under different names comparing to other payment methods.
- Time Consuming Procedures: Letter of credit is a conditional payment undertaking of the issuing bank. The condition is known as complying presentation. Making a complying presentation is not easy and a very time consuming process.
For Importers:
- Fraud Risks: While not common, it is possible that exporters can reach to the funds under letters of credit by submitting fraudulent documents.
- Higher Bank Fees: Just like exporters, importers have to pay high letter of credit fees to the banks under letters of credit transactions.
- Risks Associated with Shipment of Low Quality Goods: It is not easy to stop payment under the letter of credit once the issuing or confirming bank determines complying presentation. The importer may have to pay for the goods not consistent with the sales contract.