Dry containers, also known as general purpose containers, are by far the most common type of containers used in international sea transportation.
Almost every consumer goods that does not require a special transportation temperature can be carried out with dry containers.
Dry containers are mainly available in two sizes: 20 feet (20′) dry containers and 40 feet (40′) dry containers.
40′ dry containers are also divided into two forms: 40′ Standard Dry Containers and 40′ High-Cube Dry Containers.
On this post you can find the main differences between these two container types.
40′ Standard Dry Container vs 40′ High-Cube Dry Container
External dimensions of a 40′ standard dry container is 40′ length, 8′ width and 8’6″ height. Whereas external dimensions of a 40′ high-cube dry container is 40′ length, 8′ width and 9’6″ height.
The main difference between 40′ standard dry container and 40′ high-cube dry container is the height. 40′ high-cube container is 1′ higher than 40′ standard container in terms of external dimensions.
This external height difference also differentiates the internal height and volume of these two containers.
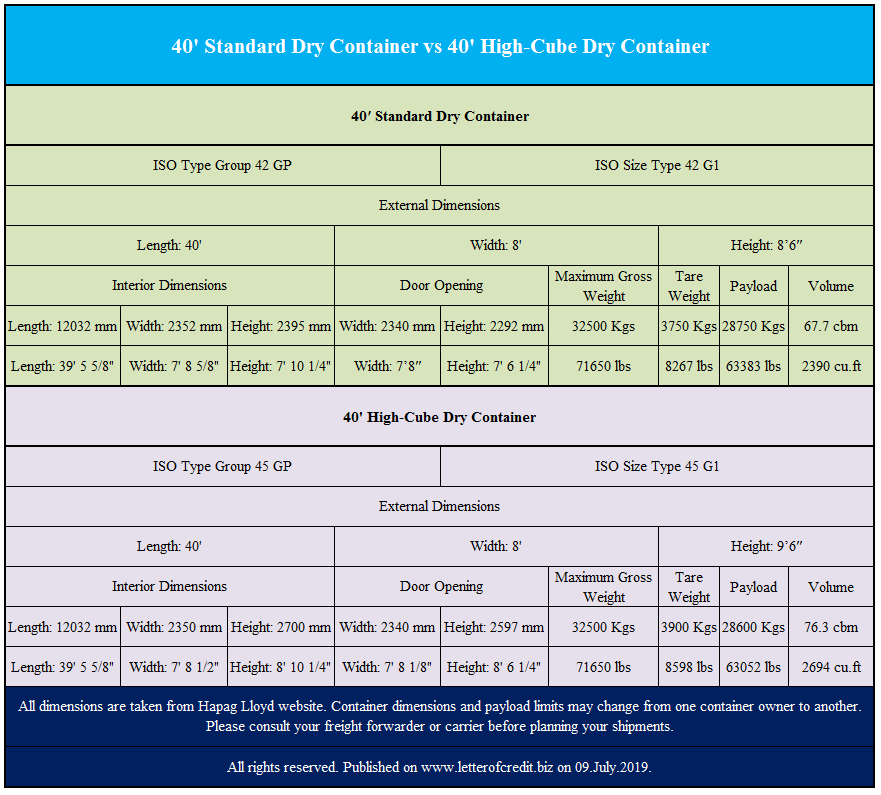 It is possible to load more goods into a 40′ standard high-cube container if the goods do not pass the allowed payload limit. Because the payload limit of a 40′ standard high-cube container is slightly less than a 40′ standard dry container.
It is possible to load more goods into a 40′ standard high-cube container if the goods do not pass the allowed payload limit. Because the payload limit of a 40′ standard high-cube container is slightly less than a 40′ standard dry container.
You can find detailed comparison between these two containers on above figure.