Under an ordinary letter of credit, the issuing bank demands a full set of clean shipped on board ocean bills of lading from the beneficiary.
But what is a full set of bill of lading according to the letter of credit rules? How does a beneficiary make sure that he presents a full set of bills of lading?
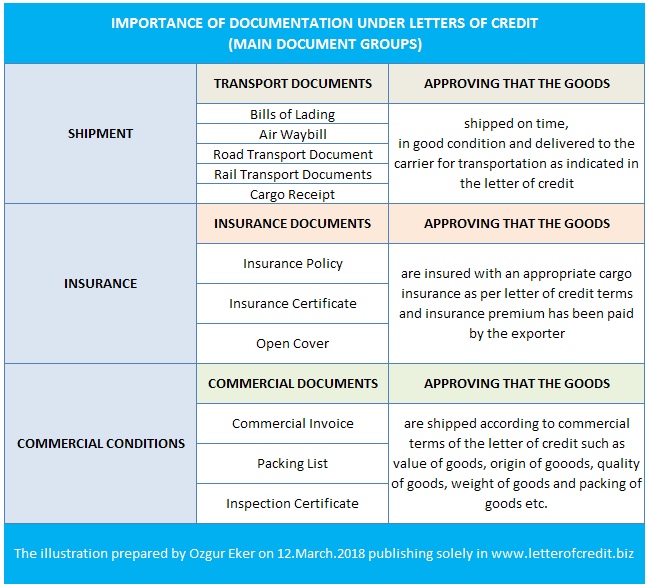
Most of the transport documents, that is subject to international transportation, issued in more than one originals.
For example, a CMR road consignment note is issued in 3 original copies. The first copy for the exporter, the second to accompany the goods; and the third for retention by the carrier. (1)
Understanding the Reasons Behind the Issuance of Multiple Original Transport Documents:
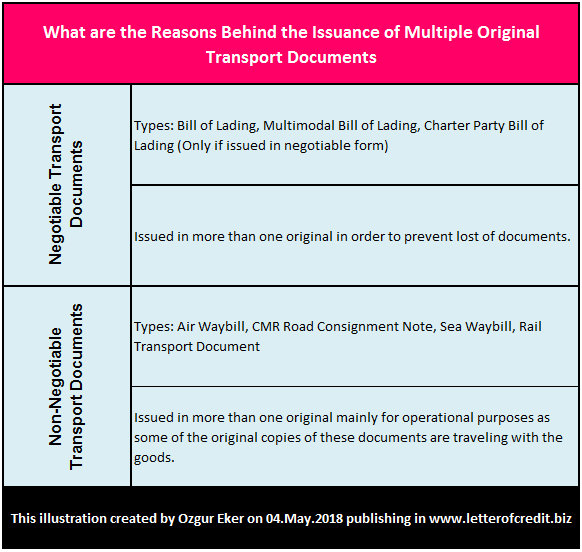
International transport documents can be classified under two main groups: Negotiable transport documents and non-negotiable transport documents.

Negotiable transport document is a title of goods, such as an original bill of lading, which can be transferred to another party by endorsement.
At least one original negotiable transport document must be surrendered to the carrier by the consignee at the place of destination to collect the goods.
Negotiable transport documents are issued in more than one originals in order to prevent lost of documents.
Non-negotiable transport document is a not a title of property and the consignment is placed at the disposal of the stipulated consignee against a proof of identity without further need to surrendering any original transport document.(2)
Non-negotiable transport documents are issued in more than one originals mainly for operational purposes as some of the original copies of these documents are traveling with the goods.
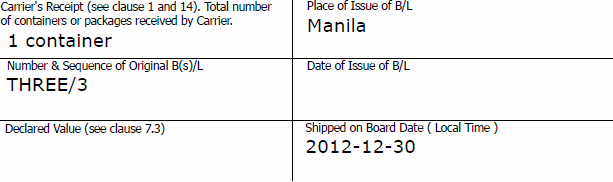
Full Set of Ocean Bills of Lading Under a Letter of Credit
According to the letter of credit rules, a bill of lading is to indicate the number of originals that have been issued and all of the originals stated on the bill of lading have to be presented by the beneficiary to the issuing bank, unless otherwise indicated in the credit.
For example, container carriers issue bills of lading in a set of 3 original and 3 copies as an established tradition for decades.
The letter of credit rules taking into account only the original bills of lading as a transport document by disregarding the non-negotiable copies.
Example:
- A letter of credit issued asking for a full set of clean ”shipped on board” negotiable bill of lading showing freight prepaid made out/endorsed to the issuing bank, notifying the issuing bank and the applicant with full address.
- The bill of lading indicated that it has issued in 3 originals.
- The beneficiary has presented all of the 3 originals as a full set of bills of lading.
Important Note: The beneficiary could have presented 3 originals and 3 copies of the bills of lading without any problem.
Letter of Credit Rules:
UCP 600 – Article 20 – Bill of Lading
iv- Be the sole original bill of lading or, if issued in more than one original, be the full set as indicated on the bill of lading.
ISBP 2007 – Full set of originals Paragraph 93
As per UCP 600 article 20 transport document must indicate the number of originals that have been issued. Transport documents marked “First Original”, “Second Original”, “Third Original”, “Original”, “Duplicate”, “Triplicate”, etc., or similar expressions are all originals. Bills of lading need not be marked “original” to be acceptable as an original bill of lading. In addition to UCP 600 article 17, the ICC Banking Commission Policy Statement, document 470/871(Rev), titled “The determination of an ‘Original’ document in the context of UCP 500 sub-Article 20(b)” is recommended for further guidance on originals and copies and remains valid under UCP 600. The content of the Policy Statement appears in the Appendix of this publication, for reference purposes. (Please keep in mind that ISBP 2007 has been updated and is not the effective version as of July 2013.)
References:
- The CMR Convention, The British International Freight Association (BIFA) Website, Retrieved: 21.06.2018
- Shipping and Incoterms, Practice Guide, UNDP Practice Series, Page:50