Transport documents can be classified under two main groups: Negotiable transport documents and non-negotiable transport documents.
Bill of lading has always been a negotiable transport document for centuries.
Road transport document, air transport document and rail transport document are relatively new transport document types and all of them are non-negotiable by their nature.
Non-negotiable transport documents generally called as waybills; such as air waybill, road waybill and rail waybill etc.
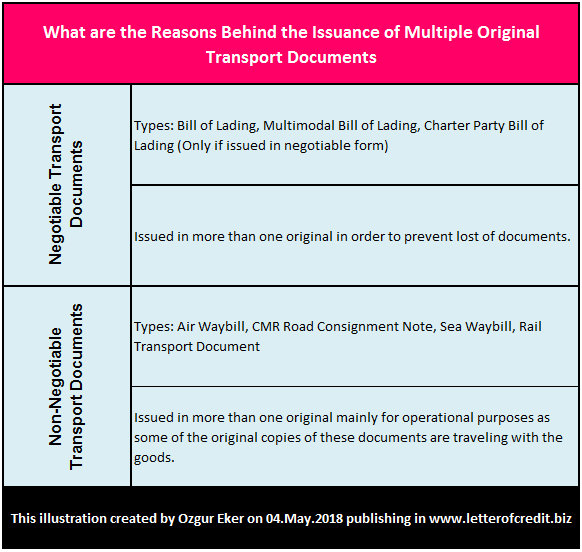
Non-negotiable transport documents share two out of three basic functions of a negotiable bill of lading:
- Non-negotiable transport documents are receipts for the goods as negotiable bills of lading;
- Non-negotiable transport documents evidence the terms of the contract of carriage (by way of clauses usually printed on one side of the document) as negotiable bills of lading;
- But non-negotiable transport documents are not said to be “negotiable documents of title” unlike negotiable bills of lading.
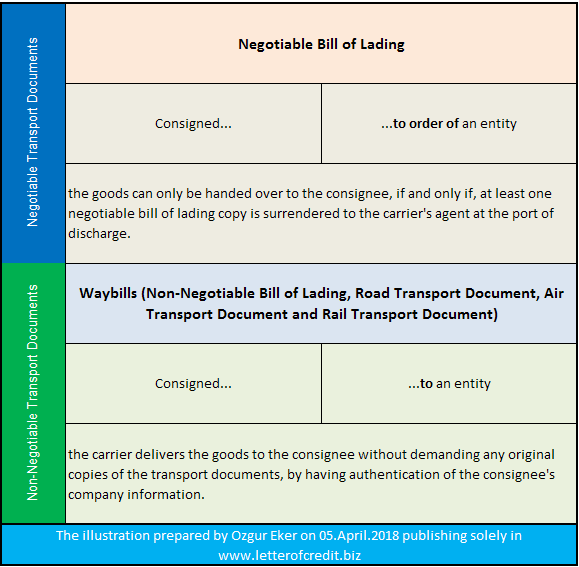
What Are The Main Differences Between a Negotiable Bill of Lading and Non-Negotiable Transport Documents?
The main difference between a negotiable bill of lading and non-negotiable transport documents is how the goods are delivered to the consignee.
Under negotiable bill of lading, the goods can only be handed over to the consignee, if and only if, at least one negotiable bill of lading copy is surrendered to the carrier’s agent at the port of discharge.
Under non-negotiable transport documents, however, the carrier delivers the goods to the consignee without demanding any original copies of the transport documents, by having authentication of the consignee’s company information.

Sea waybill is a non-negotiable bill of lading, invented by the transportation industry very recently, to respond the market, that demands a more flexible marine transport document than a conventional bill of lading.
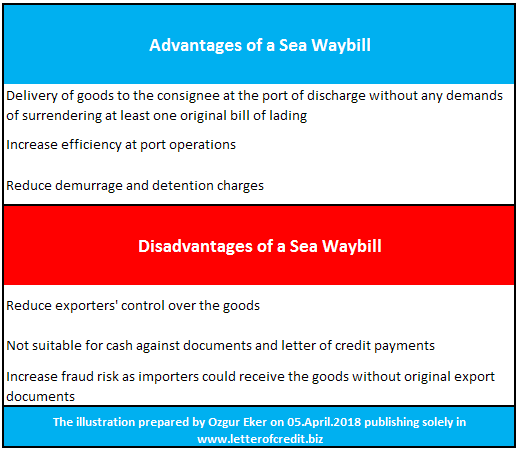
What Are The Advantages and Disadvantages of a Sea Waybill?
The main advantages of a sea waybill over a traditional negotiable bill of lading is its flexibility and ease of use.
Advantages of a Sea Waybill
Importers can clear the goods from the customs without needing to present at least one original copy of the bill of lading, when sea waybill is selected as a transport document.
This will reduce procedures and increase efficiency, and may help to eliminate or at least limit demurrage and detention charges at the port of discharge.

International trade has been increased in volume for the last couple of decades significantly; furthermore vessels are becoming faster and ports are getting quicker.
For example, one container vessel can travel around all major European Ports within a week.
It would not be possible for exporters to dispatch export documents, especially the bills of lading, within a such short period of time.
Consequently, importers may face to pay high amounts of demurrage and detention charges.
Actually, sea waybill has been invented to prevent such inefficient processes.
Disadvantages of a Sea Waybill
Main disadvantage of a sea waybill against a negotiable bill of lading is that it reduces exporter’s control over the goods, because of the fact that importer can clear the goods from customs without surrendering an original bill of lading.
This makes sea waybill not suitable for cash against documents and letter of credit payments and increases fraud risk.
How to Use Sea Waybill in Letters of Credit Transactions:
Non-negotiable Sea Waybill is covered under article 21 of UCP 600.
A non-negotiable sea waybill, however named, must appear to:
- indicate the name of the carrier and be signed by:
- the carrier or a named agent for or on behalf of the carrier, or
- the master or a named agent for or on behalf of the master.
- indicate that the goods have been shipped on board a named vessel at the port of loading stated in the credit.
- indicate shipment from the port of loading to the port of discharge stated in the credit.
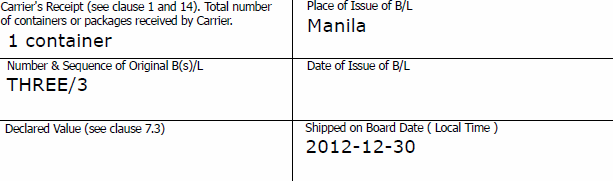
- be the sole original non-negotiable sea waybill or, if issued in more than one original, be the full set as indicated on the non-negotiable sea waybill.
- contain terms and conditions of carriage or make reference to another source containing the terms and conditions of carriage (short form or blank back non-negotiable sea waybill).
- contain no indication that it is subject to a charter party. (source : UCP 600)
Special Hints Regarding the Sea Waybill From ISBP (International Standard Banking Practice):
- To comply with UCP 600 article 21, a non-negotiable sea waybill must appear to cover a port-to-port shipment but need not be titled “Non-negotiable Sea Waybill” or similar.
- If a credit requires presentation of a non-negotiable sea waybill (“Sea Waybill”, Non-negotiable Port-to-Port transport Document” or similar) covering sea shipment only, UCP 600 article 21 is applicable.
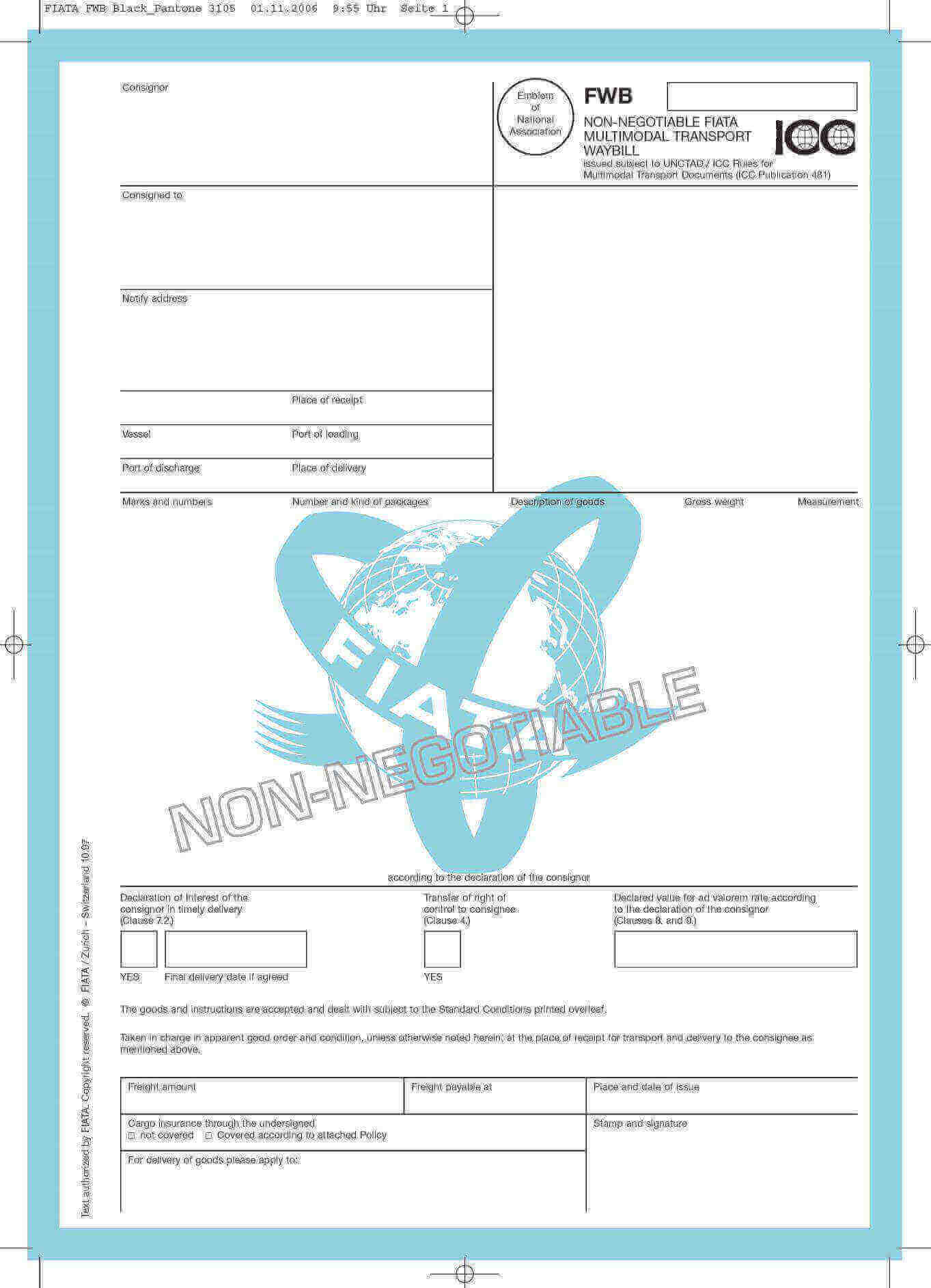
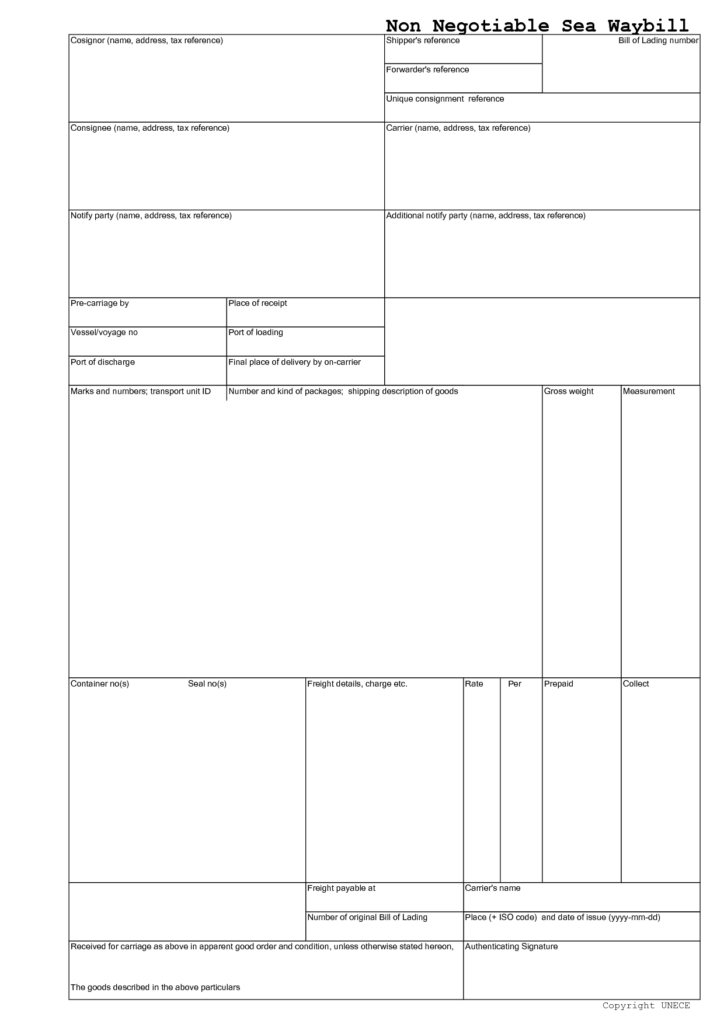
Sea Waybill Example:
You can find a sample sea waybill below in blank format.
Please keep in mind that this sea waybill format is not suitable for letter of credit, because it does not contain any reference to contract of carriage.