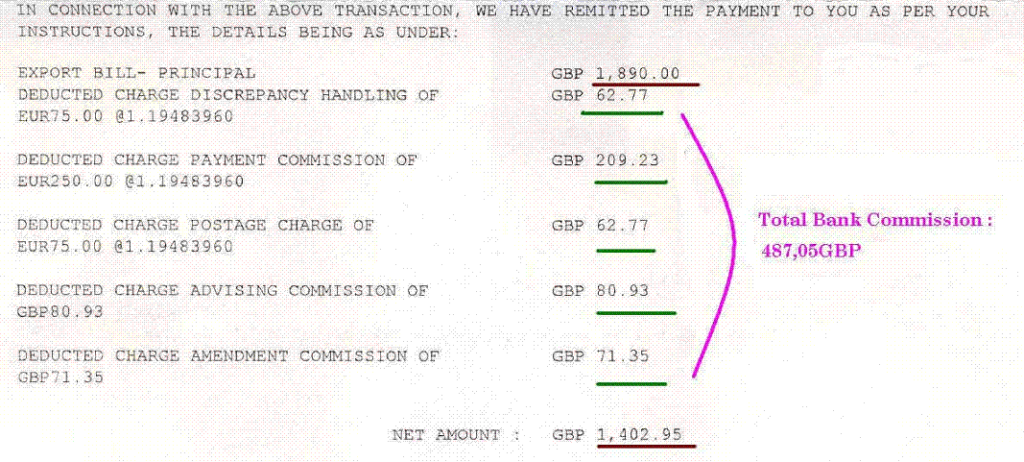
According to the letter of credit rules, a letter of credit should be issued in an irrevocable form, as a result it cannot be cancelled without the written consent of the beneficiary.
Definition of Irrevocability Concept and Its Effects on Cancellation of Letters of Credit:
According to letter of credit rules, a credit can neither be amended nor cancelled without the agreement of the issuing bank, the confirming bank, if any, and the beneficiary.
Letter of credit is a conditional payment method, which means that the payment can be made only against a complying presentation, but the terms and conditions of the credit cannot be amended or else cannot be cancelled by the issuing bank without the consent of the beneficiary.
As a result issuing banks cannot cancel letters of credit by themselves alone.
In order to cancel a letter of credit, an issuing bank has to receive a written declaration from the beneficiary certifying that the letter of credit will not be utilized.
If the letter of credit has been confirmed by another bank, the confirming bank’s written declaration should also be received before the cancellation.
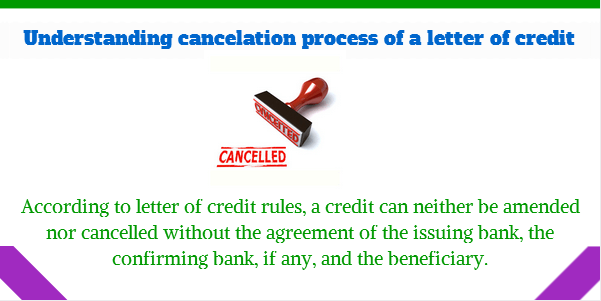
How to Cancel a Letter of Credit?
There are two ways to cancel a letter of credit.
Actually the first scenario should be treated as a “termination” rather than a “cancellation”.
Cancellation of a letter of credit which is not utilized by the beneficiary within the validity period:
Every letter of credit must have a expiry date and place.
If the beneficiary elects not to use the letter of credit within the validity period, which starts with the issuance of the letter of credit and ends with the expiry date, the letter of credit will be no longer valid.
This type of cancellation should be called as termination of letter of credit by the beneficiary.
What are the factors that may have forced the beneficiary to terminate the letter of credit?
There would be couple of factors that leads to termination of an L/C. Below you can find some reasons of termination that I can think of.
- The unit prices may have increased too much since the opening of the letter of credit and the beneficiary may perceive the transaction not profitable any more.
- The beneficiary may find the terms and conditions of the letter of credit not doable.
- Beneficiary may not be able to find required finance to perform under the letter of credit.
Cancellation of a letter of credit by the beneficiary’s written declaration within the validity period of the letter of credit:
As explained above an irrevocable letter of credit cannot be cancelled without the written consent of the beneficiary and the confirming bank, if any.
As a result, a letter of credit cancellation process should be started with the beneficiary’s written declaration.
This can be done by a letter which is issued by the beneficiary and sended direct to the issuing bank or else a swift message send by the advising bank to the issuing bank.
Case Study : Can the Issuing Bank Cancel the L/C by Himself on the Grounds That Bad Quality of Goods?
Summary: The letter of credit was issued by National Import Bank in Saudi Arabia for USD 5,500,000 allowing partial shipments.
It was planned under the sales contract that the goods will be loaded via 5 partial shipments of each equals to USD 1,100,000.
Letter of credit was available with a nominated bank located in Germany by payment. The nominated bank in Germany just advised the credit without adding its confirmation.
Additionally the nominated bank did not make any payments to the beneficiary. Its role was rather an advising bank’s role under this transaction.
The beneficiary made the 1st shipment and received the payment from the issuing bank.
On the 2nd shipment beneficiary did not get any payment from the issuing bank, although there was no advice of refusal received.
Later on the beneficiary received following message from the issuing bank via the nominated bank ‘Goods are defective, as stated by the buyer, the said L/C is cancelled.’
————————————-Message Header——————————————
Swift OUTPUT FIN 700 Issue of a Documentary Credit
Sender : NATIONALXXX
NATIONAL IMPORT BANK, THE (HEAD OFFICE) JEDDAH SAUDI ARABIA
Receiver : EXPORTXXX EXPORT BANK OF GERMANY (ALL GERMANY OFFICES) MUNICH GERMANY
————————————–Message Text ———————————————-
27 : Sequence of Total
1/1
40A : Form of Documentary Credit
IRREVOCABLE
20 : Documentary Credit Number
NATIONAL01022015
31C : Date of Issue
150102
40E : Applicable Rules
UCPURR LATEST VERSION
31D : Date and Place of Expiry
150622 GERMANY
50 : Applicant
THE NATIONAL IMPORT BANK A/C OF AL-TAJ SOAP FACTORY CO. P.O.BOX 2037 JEDDAH 21451 K.S.A
59 : Beneficiary – Name & Address
WIND TURBINES EXPORTER OF GERMANY D-28199 BREMEN, GERMANY
32B : Currency Code, Amount
Currency : USD (US DOLLAR)
Amount : #5.500.000,#
41A : Available With…By… – BIC
EXPORTXXX BY PAYMENT
43P : Partial Shipments
PARTIAL SHIPMENTS ARE ALLOWED
43T : Transhipment
TRANSSHIPMENTS ARE ALLOWED
45A : Description of Goods &/or Services
5 SETS OF WIND TURBINES
Answer: The letter of credit cannot be cancelled by the issuing bank by himself on the grounds that bad quality of goods. Only a court order could stop issuing bank to pay for the complying documents.