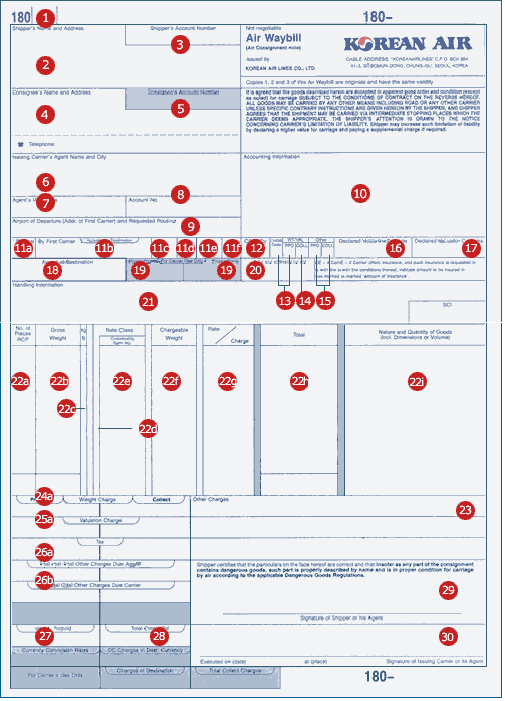
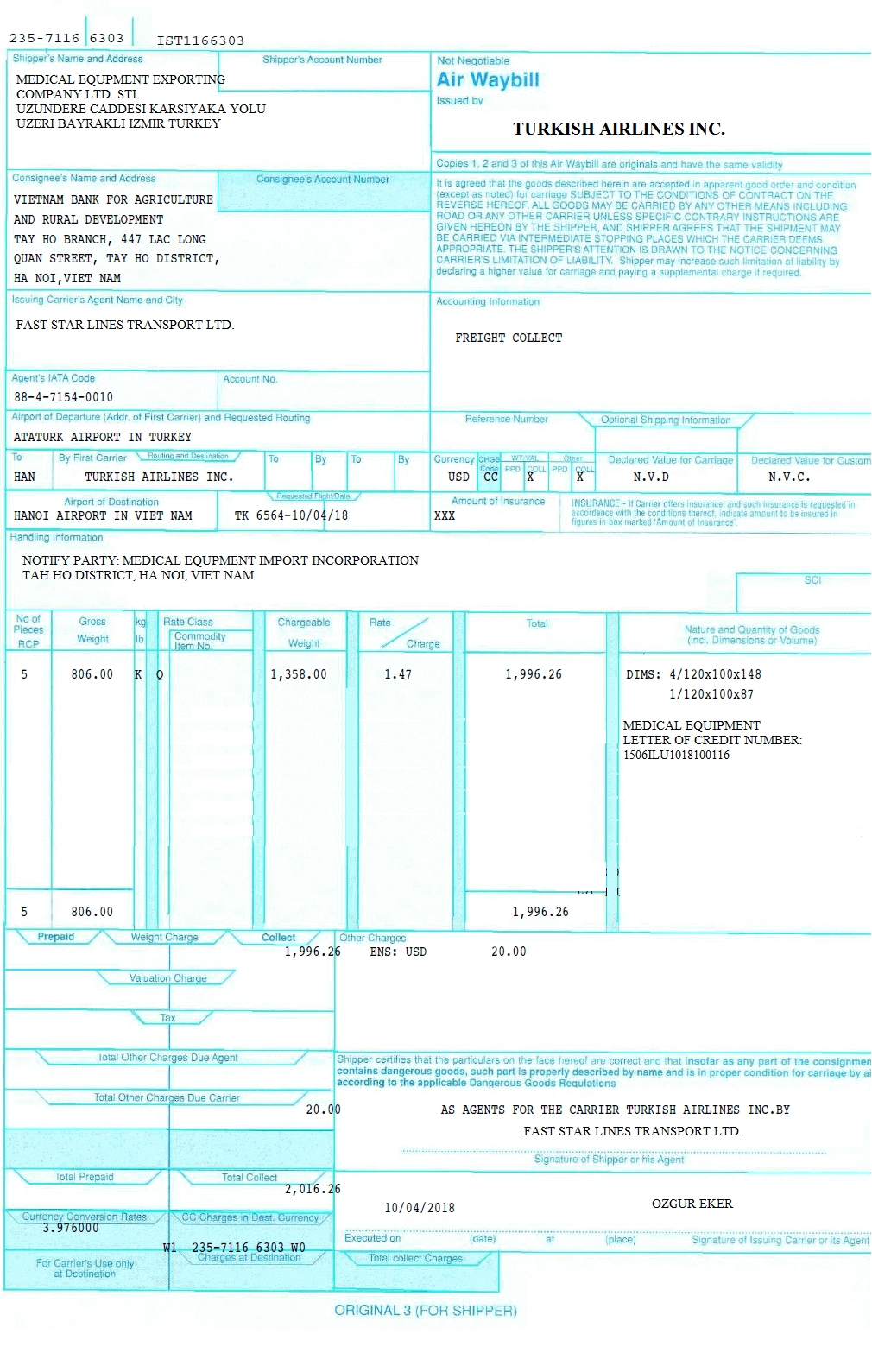
An air waybill is a document covering the carriage of goods by plane from one airport to another.
Date of shipment is one of the key definitions in a letter of credit transaction. It is used to determine
- whether shipment made on time or not (in other words a late shipment has been effected or not),
- whether documents presented within the presentation period or not (in other words a late presentation has been effected or not),
- maturity date of the time draft,
- maturity date of a deferred payment letter of credit.
Date of shipment can be determined in two ways on an air waybill.
Option 1 => There is no actual date of shipment notation on the air waybill:
- The date of issuance of the air waybill will be deemed to be the date of shipment.
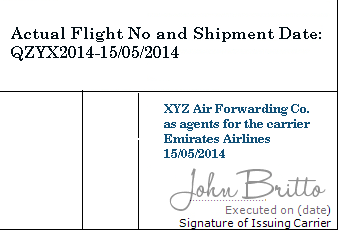
Option 2=> Air waybill indicates, by notation, the actual date of shipment: Notation date will be deemed to be the date of shipment as specified below:
- Date of the actual date of shipment notation/stamp => this date will be deemed to be the date of shipment.