On this post, I will explain Non-Negotiable Fiata Multimodal Transport Waybill, a transport document, only issued by freight forwarders, whom are the members of the FIATA (International Federation of Freight Forwarders Associations).
The FWB is an acronym which stands for “Forwarder’s Waybill”, “Fiata Waybill” or “Non-Negotiable FIATA Multimodal Transport Waybill”.
FWB is a standard format transport document, which is created by FIATA (International Federation of Freight Forwarders Associations) for general use of the freight forwarders in international freight transportation.
FWB has been restricted to use only by FIATA members.
Structure of a Fiata Waybill
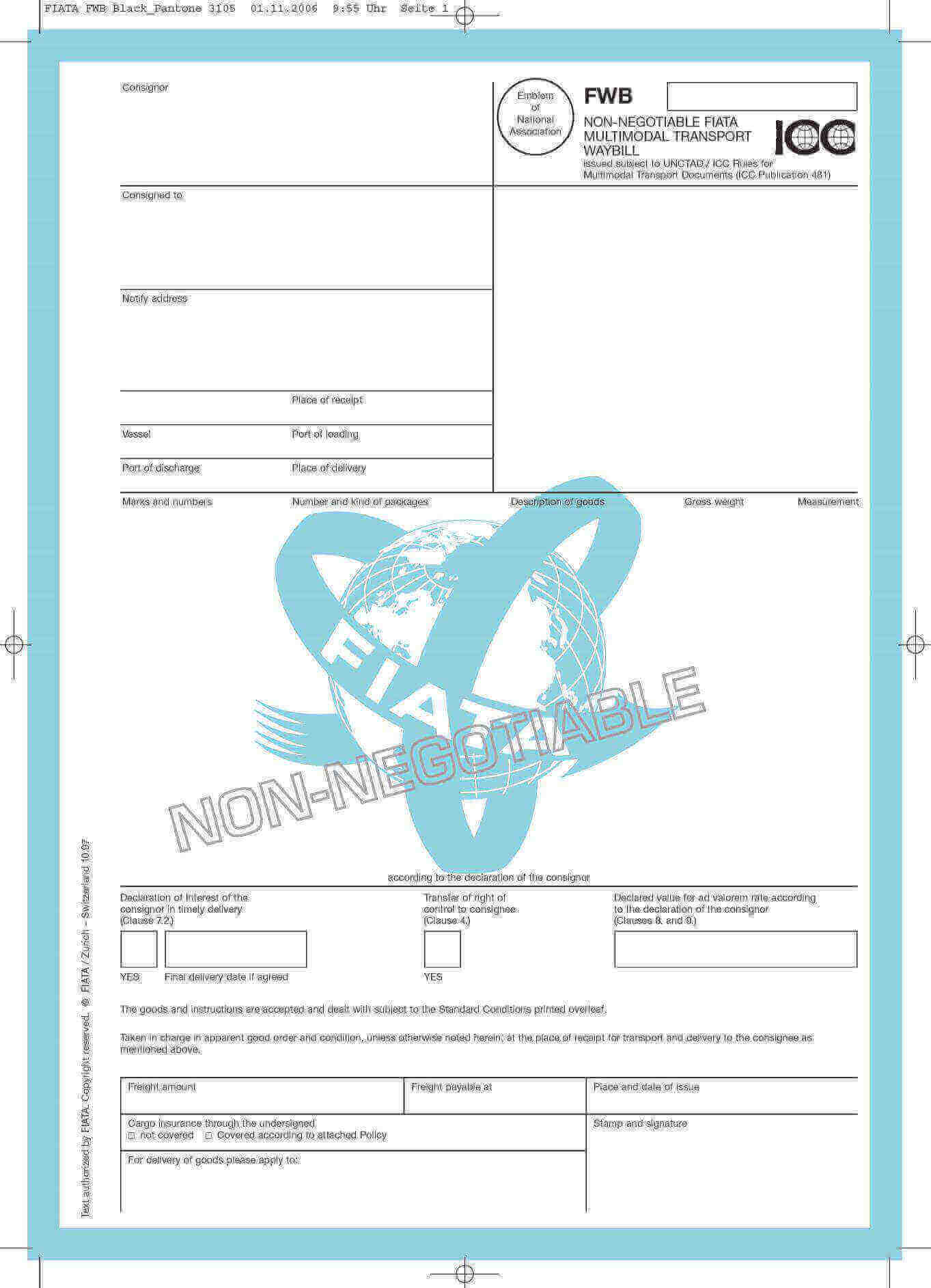
FWB is printed on a white color paper with light blue borders. Fiata logo is positioned in the middle of the FWB transport document. The ICC logo, which signifies the ICC approval, can be seen on the right up side of the document.
FWB is a non-negotiable transport document which was created by Fiata and acknowledged by ICC. This acknowledgement has been secured by the attachment of ICC logo on the right-up side of the document.
Terms and conditions of the carriage have been printed on the reverse side of the FWB transport document under the title of “Standard Conditions (1997) governing the FIATA Multimodal Transport Waybill”.
As a result FWB is not a short form or blank back non-negotiable sea waybill.
FWB is a valid transport document when it is issued as a non-negotiable sea waybill according to letter of credit rules.
This view supported by the Fiata with the following declaration: “The non-negotiable FIATA Multimodal Transport Waybill (FWB) conforms to the requirements of the “Guide for the Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (UCP 600)” of ICC (ICC publication No. 600) in line with article 21 when issued as a sea waybill, as an acceptable transport document.”
Why Exporters and Importers Use a FWB transport document?
The main reason to use a FWB would be working with a freight forwarder instead of a carrier.
FBL issued by the freight forwarders in the capacity of contractual carriers. They usually sign FBL transport document “as carrier”.
Additionally, importers could clear the consignment at the port of discharge without surrendering an original bill of lading, as carriers could deliver the cargo to the importers with a proof of identity.
What are the Main Characteristics of a Fiata Waybill?
- FWB includes a contract of carriage and it is a valid sea waybill according to current letter of credit rules.
- FWB is a non-negotiable transport document. If a FWB is issued, carriers could deliver the cargo to the importers by the proof of identity only without requiring the original copy of the FWB.
- FWB transport documents can be used not only in multimodal transportation, but also single mode port-to-port sea shipments.
- The copyrights of FBL documents are owned by FIATA. Only Fiata member freight forwarders could use FWB standard format multimodal non-negotiable waybill.
- FWB is in conformity with the UNCTAD/ICC Rules for Multimodal Transport Documents only when it is used as non-negotiable sea waybill in port-to-port sea shipments.
What are the Differences Between a FWB (Non-Negotiable FIATA Multimodal Transport Waybill) and a Shipping Line Sea Waybill (SLSWB)?
- A Shipping Line Sea Waybill (SLSWB) or carrier’s sea waybill is issued by the carrier or its agent on behalf of the carrier. SLSWB generally printed on the letterhead of the shipping line. On the reverse side of the SLSWB the terms and conditions of carriage of the shipping line are incorporated.
- A Non-Negotiable FIATA Multimodal Transport Waybill (FWB) is issued by a freight forwarder. FWB should be printed on the standard form Fiata FWB format incorporating Fiata and ICC logos. “Standard Conditions (1997) governing the FIATA Multimodal Transport Waybill” has been printed on the reverse side of the FWB. FWB signed by the freight forwarder, as carrier.