The packing list is a trade document, which shows the contents of the shipment in detail and acts as a supporting document of the commercial invoice.
The packing list may provide a means of quickly identifying merchandise required for customs inspection, give a means of determining accurate weights and measurements, and give a means for inspectors to unpack quickly to check a piece count of the contents. (1)
A packing list should state description of goods in line with letter of credit and other documents presented under the same L/C.
It should be stressed that only commercial invoice must contain exact description of goods stated in the letter of credit.
Other documents including the packing list may indicate a description of goods in general terms but not in conflict with the goods description in the letter of credit.
If the issuing bank finds out that the packing list is showing different description of goods than any other document presented, then the issuing bank raises a discrepancy, which is known as description of goods on the packing list is in conflict with other documents.
Discrepancy Example: Description of Goods is in Conflict with Other Documents
A letter of credit has been issued in SWIFT format, subject to UCPURR latest version, with the following details:
Letter of Credit Conditions
Field 45A: Description of Goods and or Services: 2500 Kgs Mild Dutch Cheese with 25% less salt content. Delivery Terms: FOB Amsterdam Port, Holland Incoterms 2010.
Field 46A: Documents Required:
- Hand signed commercial invoice in three originals all duly stamped indicating description of goods as per proforma invoice no COMINV12345 dated 05.06.2014.
- Certificate of origin ‘EUR.1’ in one original and one copy issued by competent authority showing Netherlands origin of the goods.
- Packing list in three folds evidencing the content of each package of the shipped goods.
- Full set clean on board bill of lading, issued to the order of applicant (with full address), marked freight collect, notify applicant (with full address – phone ++3122190700) (Bill of lading showing additional freight charges is not acceptable).
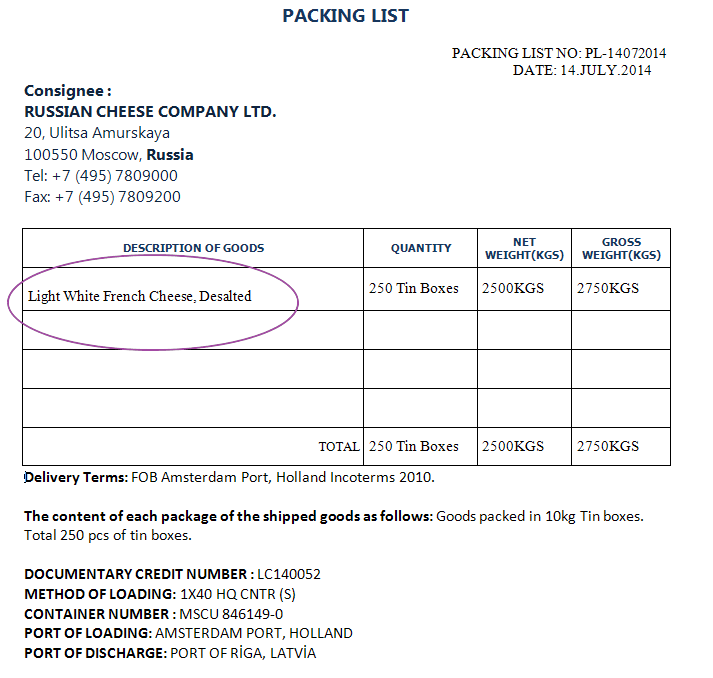
- The beneficiary presented a Packing List as shown on the below picture.
Packing List
Discrepancy: The letter of credit requires shipment of “Mild Dutch Cheese with 25% less salt content”, but the packing list describes the goods as “Light White French Cheese, Desalted”, the description is representing a change in nature, classification or category of the goods.
Reason for Discrepancy: Description of goods on the packing list should be shown in general terms but not in conflict with that stated in the letter of credit or another document.
Sources:
- Transportation Best Practices Manual, Canadian Manufacturers and Exporters Newfoundland and Labrador Division, prepared by PF Collins International Trade Services, 2003, Page:22