What Does Negotiation Mean?
Negotiation means the purchase by the nominated bank of drafts (drawn on a bank other than the nominated bank) and/or documents under a complying presentation, by advancing or agreeing to advance funds to the beneficiary on or before the banking day on which reimbursement is due to the nominated bank.
What Are the Benefits of a Negotiable Letter of Credit to the Exporters?
Exporters can reach the payment sooner with negotiable letters of credit, while offering usance terms to the importers.
With the help of the negotiable letters of credit, exporters can balance their cash flows, and able to propose competitive payments terms to the importers.
Who Should Pay Negotiation Fees?
Negotiation fees generally covered by the exporters, although this is contrary to the letter of credit rules.
How to Understand if a Letter of Credit Negotiable or Not?
In order to understand if a letter of credit is negotiable or not, you need to look at field “41A-Available with/by” field in a MT700 swift message.
If letter of credit is negotiable, it must be mentioned under field 41A that the letter of credit is available by negotiation.
How Does a Negotiable Letter of Credit Work?
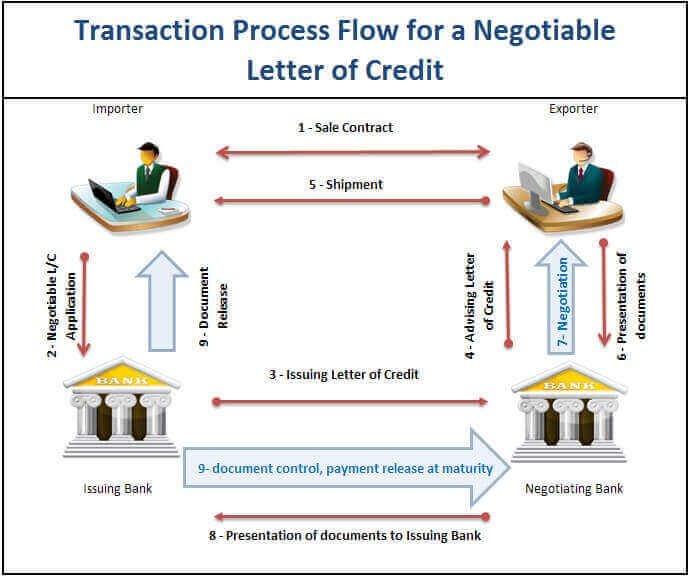
- Step 1: Exporter and importer enter into a sales contract by agreeing on the terms and conditions of the business transaction.
- Step 2: Importer contacts to the issuing bank for the issuance of the negotiable letter of credit.
- Step 3: Issuing bank issues negotiable letter of credit in swift format and sends it to the nominated bank, who is also negotiating bank and advising bank.
- Step 4: Negotiating bank advices the letter of credit to the exporter. Exporter checks the letter of credit conditions, if they are acceptable to the exporter, he starts production of the goods.
- Step 5: Exporter ships the goods within the validity of the letter of credit and not later than latest date of shipment indicated in the L/C.
- Step 6: Exporter presents the documents to the negotiating bank within the presentation period allowed under the letter of credit. Remember if presented documents contain a transport document, presentation must be completed within 21 days after date of shipment.
- Step 7: Negotiating bank checks the documents presented by the exporter and, if determines that they are compliant, advances cash to the exporter. The “negotiation” is effectively the purchase of documents from the exporter at a discount.
- Step 8: Negotiating bank presents the documents to the issuing bank.
- Step 9: Issuing bank checks the documents and, if compliant, accepts them to be paid to the negotiating bank at maturity. At the same time, issuing bank gets in touch with the importer and delivers documents to him according to the financial agreement between the issuing bank and the importer.
Sample Negotiable Letter of Credit Swift Message
————————————- Message Header ——————————————-
Swift OUTPUT FIN 700 Issue of a Documentary Credit
Sender : COBADEFFXXX
COMMERZBANK AG
(HEAD OFFICE)
FRANKFURT AM MAIN DE
Receiver : BOBIHKHH
BANK OF BARODA, HONG KONG
Hong Kong HK
————————————- Message Text———————————————–
27: Sequence of Total
1/1
40A: Form of Documentary Credit
IRREVOCABLE
31C: Date of Issue
140922
40E: Applicable Rules
UCP LATEST VERSION
31D: Date and Place of Expiry
05FEB15 HONG KONG
41A: Available With…By… – BIC
ANY BANK
BY NEGOTIATION
42C: Drafts At
AT 90 DAYS AFTER BL
42A: Drawee
BOBIHKHH