Nominated bank is another important yet not well understood term in international letter of credit transactions.
May be the biggest contribution of this lack of understanding comes from the blur definitions of its roles and responsibilities comparing to the confirming bank, advising bank or issuing bank under the letter of credit rules.
On this post I will try to explain you one of the most challenging term in international letter of credit transactions: Nominated Bank.
Here are the headlines of the article:
- What is a nominated bank?
- What are the responsibilities of the nominated bank?
- Which UCP 600 article regulates the nominated banks responsibilities?
- What are the differences between the nominated bank and the advising bank?
- What are the differences between the nominated bank and the confirming bank?
What is a Nominated Bank?
Nominated Bank means the bank with which the letter of credit is available or any bank in the case of a credit available with any bank.

What are the Responsibilities of the Nominated Bank?
According to the letter of credit rules a letter of credit must state the bank with which it is available.
Alternatively, it is possible to open a letter of credit to be available with any bank. These kinds of letters of credit are known as “freely negotiable letters of credit”.
The bank with which the letter of credit is available is defined as a nominated bank.
UCP 600 defines the responsibilities of a nominated bank in two main categories:
- Payment Responsibility
- Acceptance of Presentation Responsibility

Payment Responsibility:
Provided that the stipulated documents are presented to the nominated bank and that they constitute a complying presentation, the nominated bank should honor if the credit is available by sight payment, deferred payment or acceptance with a nominated bank.
Alternatively, the nominated bank can negotiate the complying presentation if letter of credit is available by negotiation with the nominated bank.
But it is worth mentioning that unless a nominated bank is the confirming bank, an authorization to honor or negotiate does not impose any obligation on that nominated bank to honor or negotiate, except when expressly agreed to by that nominated bank and so communicated to the beneficiary.
In daily practice, nominated banks rarely pay to the beneficiaries against the complying presentation.
What they commonly do is just to receive the documents from the beneficiaries and send them to the issuing banks by demanding reimbursement either from the issuing bank or reimbursing bank.
They transfer the letter of credit amount, which they have received from one of these two banks to the beneficiaries.
Acceptance of Presentation Responsibility:
If a letter of credit is available with a nominated bank, then the authorized nominated bank should accept the presentation of the beneficiary.
Once again please kindly keep in mind that the acceptance of presentation does not give any payment obligation to the nominated bank.
By presenting documents to a bank in their own country, beneficiaries could complete their presentations faster. This is one of the biggest advantages of using a nominated bank for the beneficiaries.

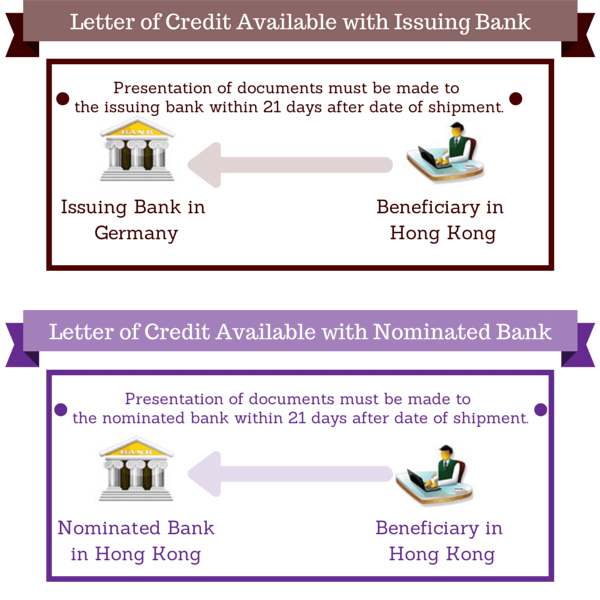
Case Study: Presentation of Documents Where the Letter of credit is Available with the Issuing Bank

———————————- Analysis of the Example ————————————-
The letter of credit is available with the issuing bank in Germany. The beneficiary is located in Hong Kong.
The beneficiary has to collect all required documents and complete the presentation within 21 days after the date of shipment.
21 days of presentation period includes express courier transit time between Hong Kong and Germany.
The problem with such a letter of credit structure is that in case the issuing bank finds discrepancies on the documents, it would be almost impossible for the beneficiary to correct the documents and re-submit the corrected documents for a timely presentation.
On below figure you can see the difference between letter of credit which is available with the issuing bank and the nominated bank.

Which UCP 600 Article Regulate the Nominated Bank’s Responsibilities?
UCP 600 article 12 defines the roles and responsibilities of the nominated bank. Additionally nominated bank’s liabilities have been described in numerous articles under UCP 600.
What are the Differences Between the Nominated Bank and the Advising Bank?
The advising bank has no payment obligations under the letter of credit rules.
The advising bank has two main responsibilities: authenticating incoming letters of credit and transmitting them to the beneficiaries as a whole, intact.
Additionally, an advising bank has no connection with the letter of credit availability or the place of letter of credit expiry.
On the other hand the nominated bank is the bank with which the letter of credit is available, as a result the letter of credit expires at the counters of nominated bank.
Furthermore the issuing bank authorizes the nominated bank to honor or negotiate the complying documents that are presented to them.
What are the Differences Between the Nominated Bank and the Confirming Bank?
First of all, please kindly be noted that according to the letter of credit rules it is possible that the nominated bank and the confirming bank could be different banks.
But in practice a bank would not add its confirmation to the letter of credit, if it is not available with itself.
As per letter of credit rules the confirming bank has clear payment obligations.
If the presentation is complying, then the confirming bank must honor. It is a very straight forward definition.
But nominated banks may or may not pay against the complying presentations. If they do not, then either confirming bank or issuing bank must pay.
Case Study: Negotiation of a draft by a nominated bank, which is drawn under a letter of credit

Negotiation under letters of credit is an old “habit” which was invented long before even the first version of the UCP existed.
I am told that negotiation was used by London merchant bankers when UK exporters shipped goods covered by credits issued in Hong Kong or Shanghai.
At that time, credits were (normally) not advised through a bank (in London), and there was no nominated bank.
The presentation of documents was to be made at the counters of the issuing bank, which, after it examined and approved the documents, transferred the relevant amount to the beneficiary.
That took a long time. To assist the exporter – and of course to make money – the merchant banks offered to negotiate the documents. They discounted the bill of exchange, mostly with recourse. (“Negotiation” seen to be no benefit to beneficiaries, Reinhard Längerich, DCInsight Vol. 10 No.2 April – June 2004)
UCP 600 defines negotiation as follows:
- “Negotiation means the purchase by the nominated bank of drafts (drawn on a bank other than the nominated bank) and/or documents under a complying presentation, by advancing or agreeing to advance funds to the beneficiary on or before the banking day on which reimbursement is due to the nominated bank.”
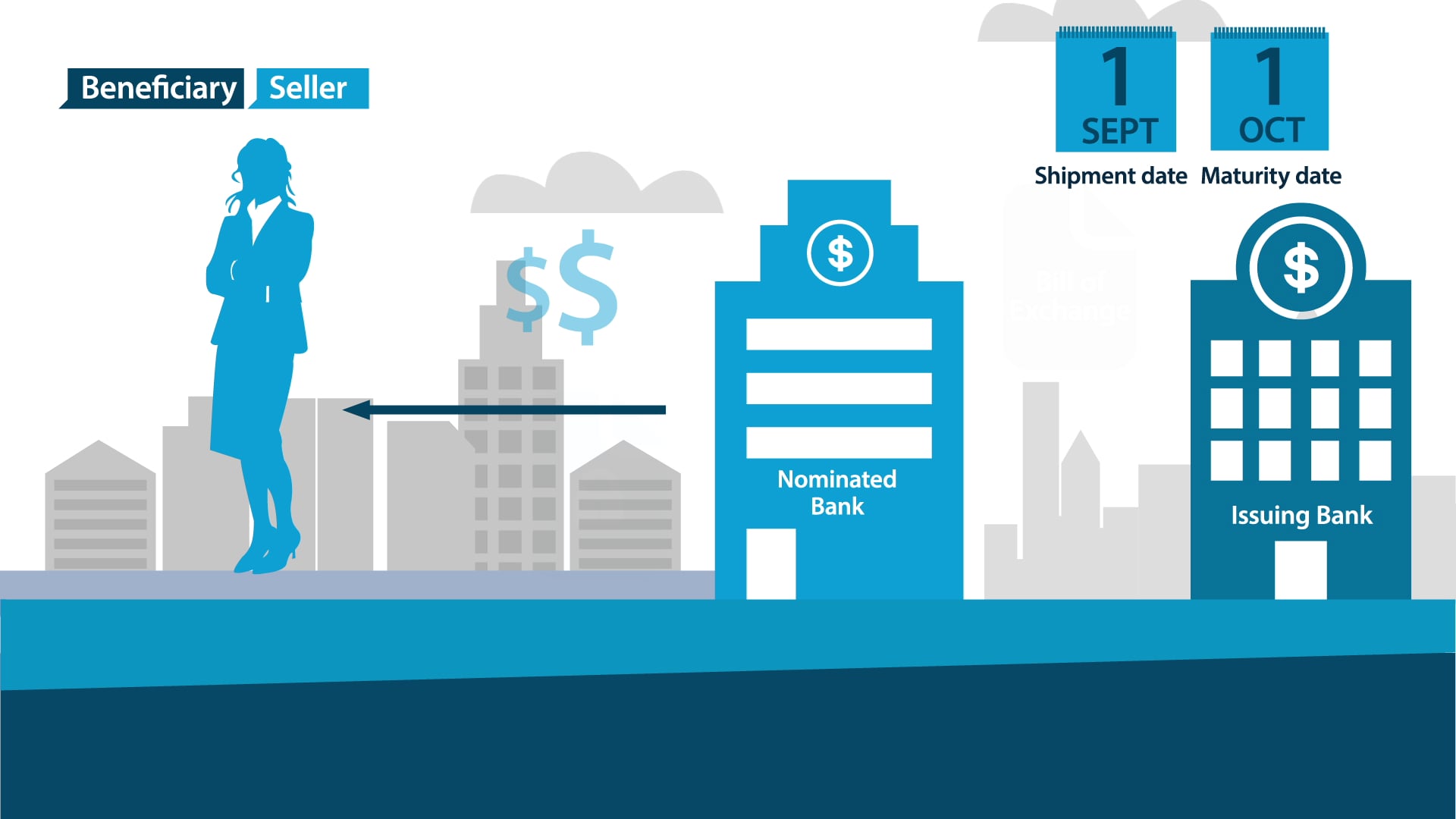
I would like to show an example of the negotiation of a draft which is drawn under a letter of credit with the face value of EUR 100.000,00 as illustrated below.

ABN AMRO Bank is the nominated bank.
The beneficiary endorses the draft to ABN AMRO Bank, and ABN AMRO Bank discounts the draft by paying to the beneficiary EUR 95.000,00.
The transfer of the funds from the ABN AMRO Bank to the beneficiary constitutes a negotiation.
ABN AMRO Bank presents the draft and other letter of credit documents to the Issuing Bank.
If Issuing Bank determines that the presentation is complying, then the issuing bank must pay EUR 100.000,00 to ABN AMRO Bank.
If ABN AMRO Bank could not get the face value of the draft from the Issuing Bank, then ABN AMRO Bank may go back to Beneficiary to recover its EUR 95.000,00 payment.
ABN AMRO Bank, which is the nominated bank, discounts and pays the discounted letter of credit amount to the beneficiary with recourse basis. Do you want to know more about with recourse term? Please click here for more information.